Conduction Heat Transfer
Conduction heat transfer is transfer of thermal energy from more energetic to less energetic particles due to their interaction.
Example :
A one side steel plate is exposed to Bunsen burner; molecules get more energy from that heat and start to vibrate. They vibrate, interact with their neighbors exchanging energy and this energy goes from the hot side to the cold side, by conduction.
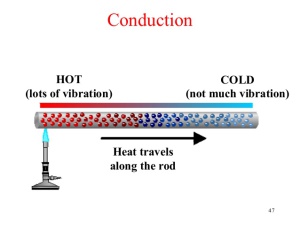
Figure 01 - Representation of Conduction
Heat transported through a stationary medium (solid or fluid without motion) by vibrational energy of molecules that increase with temperature.
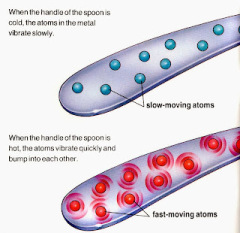
Figure 2 - Slow and fast motion of atoms