-
Hide blocks
- Full screen
- Standard view
Topic outline
Topic 1
Target public: 2nd year Process engineering/ Semester: 3
Teaching Unit: UEF 2.1.2
Course title: Mineral Chemistry
Credit: 4
Coefficient: 2
Duration: 15 weeks
Weekly timetable: - 1h 30 min course +1h 30min tutorial group
Place of teaching: classroom 23 for the course and classroom 1 for tutorial group
Evaluation methods: - Final exam 60%
- Continue evaluation 40%
Teacher: Dr. Merzouki Soraya
Contact: s.merzouki@centre-univ-mila.dz
Availability: every day at head of department officeEducational Objectives:
Provide the basic concepts of inorganic chemistry
Learning of some methods such as crystallography and synthesis.CHAPTER 1:Review of Some Important Definitions
Mole
Molar mass
Molar volume
Mole fraction
Mass fraction
Volume fraction
Density
specific gravity
Relationship between mass fraction and mole fraction
Material balance: Concept of reactant and excess reactant, Concept of excess percentage, Concept of conversion percentage.
for more explication in chapter 1 you can ask using the following link
CHAPTER 2: CRISTALLOCHEMISTRY

Definitions
Crystal
Polyhedron
Crystalline lattice
Cell: motif, crystallographic sites, coordination number
Crystalline system
Crystallographic computations :
direction& plan (Miller Indices), distance, angle, density (multiplicity , compactness)
Some examples of crystalline structures:
metallic, ionic, covalent.
Molecular structure: ice structurePeriodicity and In-Depth Study of the Properties of Elements
Historic review about Mendeleev Table
Periodic Classification
Groups A in the periodic table:
Alkaline Metals (IA)
Alkaline Earth Metals (IIA)
Boron family (IIIA)
Carbone family (IVA)
. Nitrogen family (VA)
-Chalcogen family: (VIA)
. Halogens family (VIIA)

CHAPTER 4:THE MAJOR METTALURGIES

Definitions
Metallurgy
Ores
subject of metallurgy
Mineral dressing
Chemical metallurgy
Physical metallurgy
Mechanical metallurgy
Powder metallurgy
the major metallurgy
Iron (Fe)
Titanium (Ti)
Copper (Cu)
Magnesium (Mg)
CHPTER 5: THE MAJOR MINERAL SYNTHESIS
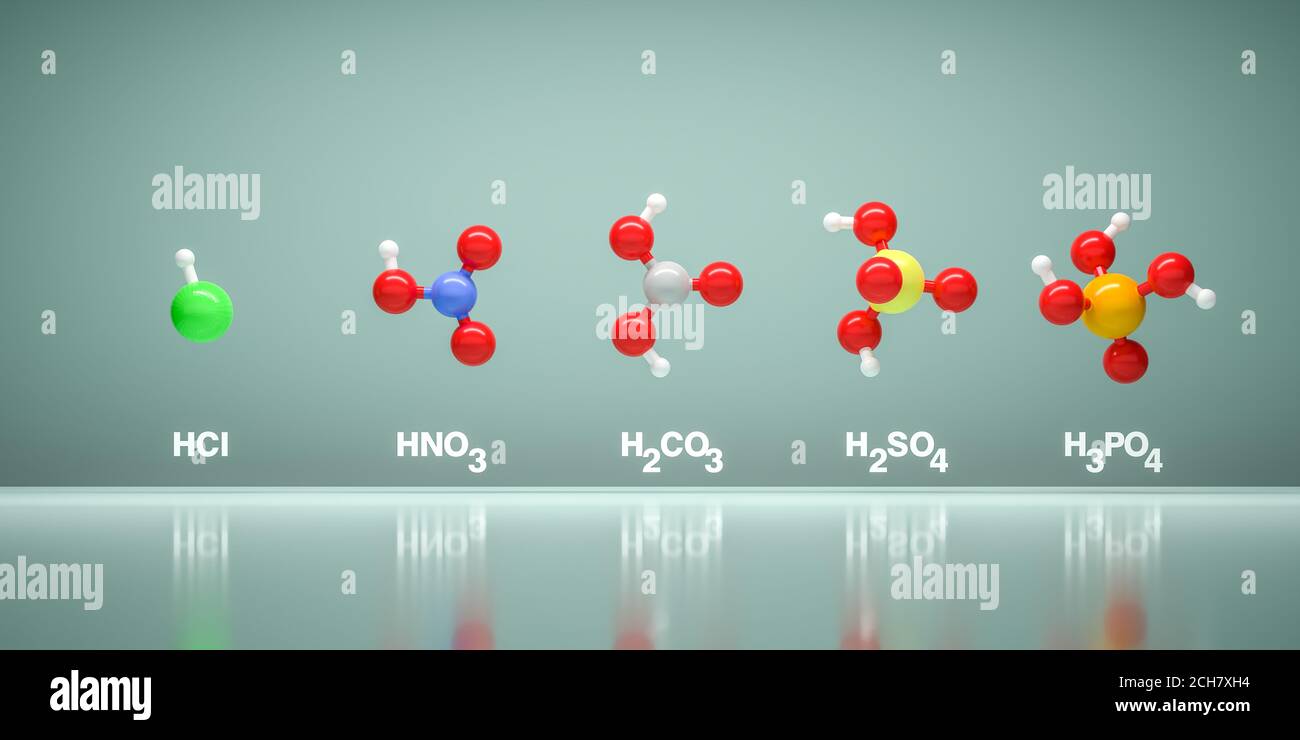
Sulfuric acid H2SO4
phosphoric acid H3PO4
ammonia NH3
nitric acid HNO3REFERENCES
- Lalaymia youcef, cours chimie minérale pharmaceutique, departement de pharmacie, université de Batna , 2020.
- Donald E. Sands, Introduction to cristallography,DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC , NEW YORK, USA, 1993.
- Bouchiba nabila, cours de chimie minérale et application , université Ahmed Ben Bella, Oran.
- Andrée Harari et Noël Baffier, DES SYMÉTRIES AUX PROPRIÉTÉS , Fondation de la maison de chimie, 2015.
- R.-B. Li et al, MPROVEMENT OF MODELING ON THE PIDGEON PROCESS FOR MAGNESIUM PRODUCTION BY INTRODUCING THE VARIABLE THERMOPHYSICAL PROPERTIES. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B-Metall. 58 (3) (2022) 451 - 459.
- Marck E. Schlesigner et al, Extractive Mettalurgy of cupper, 5th edition, Elseiver, 2011
- European Fertilizer Manufacturers’ Association, PRODUCTION OF AMMONIA, Ave. E van Nieuwenhuyse 4, B-1160 Brussels, Belgium. 2000.
- Donald Parnell, P.E., Basic Principles of Metallurgy and Metalworking. Woodcliff Lake, NJ 07677
